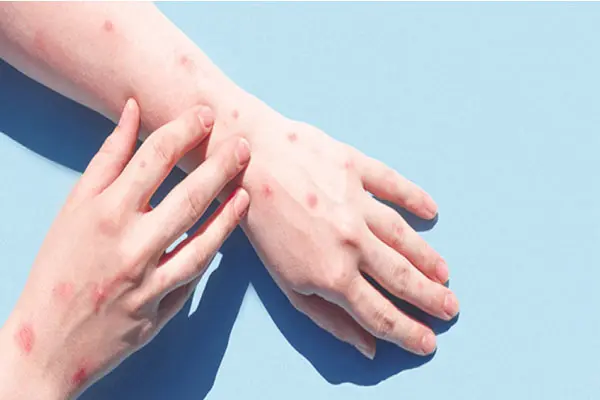
猴痘病毒通常流行於中非與西非的熱帶地區。然而, 目前爆發的中心是在歐洲。
MP3:
焦點新聞
On July 6, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced plans to hold a second meeting to discuss the growing number of monkeypox cases seen around the world. In a statement in early July, the WHO director-general said there had been over 6,000 cases in 58 different countries. While the monkeypox virus was listed as a public health concern at the previous meeting, it has yet to be elevated to a global health emergency.
The monkeypox virus is usually endemic to tropical regions of Central and West Africa. However, the current epicenter of the recent outbreak is in Europe. Symptoms of the disease include fever, muscle aches, and a skin rash or skin lesions. The virus is spread through close physical contact. Using clothing, towels, and other items that have come into contact with an infected person’s skin can also lead to infection.
中文翻譯
世界衛生組織(WHO)於七月六日宣布舉行第二次會 議的計畫,以討論全球目前不斷增加的猴痘案例。在七月 初的聲明中,世衛祕書長表示在五十八個不同國家中,已 出現六千多個病例。雖然在前一次會議中,猴痘病毒被列 為公共衛生事件,但它還未被升級至全球衛生緊急事件。
猴痘病毒通常流行於中非與西非的熱帶地區。然而, 目前爆發的中心是在歐洲。該疾病的症狀包括發燒、肌肉 疼痛以及皮疹或皮膚損傷。這種病毒是透過親密的肢體接 觸傳播的。使用接觸過染疫者皮膚的衣服、毛巾和其他物 品也可能會感染。

[此文章售價 1 雅幣已有 0 人購買]
若發現會員採用欺騙的方法獲取財富,請立刻舉報,我們會對會員處以2-N倍的罰金,嚴重者封掉ID!












